Hybrid arch frozen elephant trunk repair: evidence from the Canadian Thoracic Aortic Collaborative
Abstract
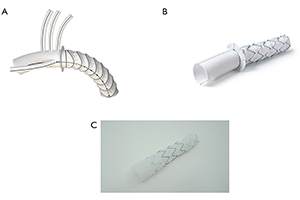
Background: The frozen elephant trunk (FET) technique has become an increasingly popular strategy for aortic reconstruction in the setting of extensive thoracic aortic aneurysms or dissections. The objective of this study is to report on the Canadian experience with the FET technique in both the elective and emergent settings.
Methods: A total of 167 consecutive patients (mean age 65±13 years, 30% female, 25% re-operation) underwent elective (70%) and non-elective (30%) aortic arch reconstruction with the FET technique between May 2008 and October 2019 in six centers of the Canadian Thoracic Aortic Collaborative (CTAC). In-hospital clinical endpoints and early imaging endpoints were prospectively collected and analyzed.
Results: All 167 patients underwent successful FET implantation. In-hospital mortality occurred in 14 patients (8%), stroke occurred in 22 patients (13%) and temporary and permanent spinal cord ischemia (SCI) occurred in 6 (3.6%) and 3 (1.8%) patients, respectively. Prolonged mechanical ventilation was required in 35 patients (21%), renal failure requiring dialysis in 14 patients (8%) and atrial fibrillation in 59 patients (36%). The median hospital and intensive care unit (ICU) lengths of stay were 3 [interquartile range (IQR): 1, 6] and 10 (IQR: 7, 17) days, respectively. The rate of type 1A endoleak was 3.6%, with the lowest rate in patients who underwent a total arch replacement with a hybrid FET graft (0%) and the highest among patients who had a hemiarch with antegrade thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR) deployment (25%). The rate of other types of endoleak and stent complications was comparatively low.
Conclusions: The early CTAC experience with the FET operation demonstrates technical feasibility and good early clinical outcomes in elective and emergent patients. Further analysis is required to explore variations in technique and their potential impact on early and late outcomes.
Cover