Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension: diagnosis, operability assessment and patient selection for pulmonary endarterectomy
Abstract
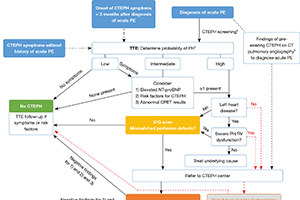
Healthcare providers outside pulmonary hypertension (PH) centers having misinformation or insufficient education, whilst a general lack of treatment awareness contribute to a massive underdiagnosis of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH), diagnostic delay and refusal of surgery by patients. Together with the subjective operability assessment, this leads to too few patients undergoing a pulmonary endarterectomy (PEA); even though this surgery results in an improved survival and exercise capacity. Acute pulmonary embolism (PE) survivors should undergo a CTEPH screening strategy. Patients screened positive and those with CTEPH symptoms (with or without history of PE), should undergo transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) to determine the probability of PH. High PH probability patients should undergo a ventilation/perfusion (V/Q) scan. A negative scan rules out CTEPH. Patients with a positive V/Q scan, but also patients with findings suggestive for CTEPH on computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) to diagnose acute PE, should be referred to a CTEPH center. Further diagnostic work-up currently consists of catheter based pulmonary angiography, CTPA and right heart catheterization. However, new imaging technologies might replace them in the near future, with one single imaging tool to screen, diagnose and assess operability as the ultimate goal. Operability assessment should be performed by a multidisciplinary CTEPH team. PEA surgery should be organized in a single center per country or for each forty to fifty million inhabitants in order to offer the highest level of expertise. Informing patients about PEA should preferably be done by the treating surgeon. Based on the estimated incidence of CTEPH and with a better education of patients and healthcare providers, despite the advent of new interventional and medical therapies for CTEPH, the number of PEA surgeries performed should still have the potential to grow significantly.
Cover