Current state of hybrid solutions for aortic arch aneurysms
Abstract
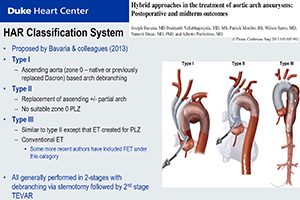
Since its inception in the early 2000s, hybrid arch repair (HAR) has evolved from a novel approach to a well-established treatment modality for aortic arch pathology in appropriately selected patients. HAR procedures have been proposed as a means to circumvent the perioperative morbidity and mortality associated with open total arch replacement. These procedures, all of which remain off-label applications of approved endograft technology, combine more conventional open surgical techniques, to create endograft landing zones, with thoracic endovascular aortic repair to exclude the aortic pathology from the circulation. The current classification system for HAR was proposed in 2013 and consists of three types, designated by the Roman numerals I, II and III. The current system has become outdated, however, with the advent of newer technologies, and herein we propose a new, updated classification system that is more encompassing with regards to the broad array of options available to treat aortic arch disease. Likewise, an institutional algorithm to guide patient and operative selection for HAR is presented. Patients are considered for HAR if they have either high-risk comorbidities or high-risk anatomy, with an important feature of the algorithm being that any decisions about repair strategy should be made by a surgical team with expertise in both open and endovascular techniques. Despite being performed for nearly two decades, the evidence around HAR consists mainly of single center series (level B–C evidence) with no randomized controlled trials. The data suggest HAR to be a safe alternative to open repair with acceptable short and mid-term results. As we as aortic surgeons continue to move towards less invasive approaches, both conventional open and hybrid techniques will remain important tools in the toolbox for arch repair, although the advent of multi-branched arch endografts will almost certainly reduce the extent of open or hybrid repair in many patients and eliminate it altogether in others.
Cover