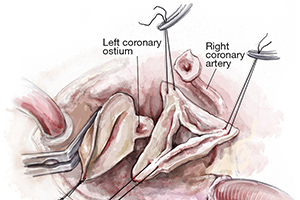
Bicuspid aortic valve repair: the 180°-Reimplantation technique
Abstract
Bicuspid aortic valves (BAVs) represent a wide spectrum of aortic valve phenotypes. We have therefore previously proposed a new repair-oriented surgical classification for BAVs in order to facilitate our understanding of any given phenotype and to guide surgical repair. BAVs can range from symmetric to very asymmetric, and classification is determined by commissural orientation. This can therefore range from 180° to 120° respectively, and as such has further implications for the presence or absence of a raphe; the height of the non-functional commissure (raphe); the length of the line of cusp fusion; and the architecture of the aortic valve sinuses. Over the last three decades, we have attempted different repair strategies for BAVs, with its respective learning curves and have achieved the best long-term repair results with our signature approach: the 180°-Reimplantation technique (El Khoury technique). Although very asymmetric and tricuspid aortic valve-like phenotypes are sometimes best repaired through tricuspidization, we have found that the majority of BAVs are amenable to our 180°-Reimplantation technique. This technique creates a symmetric valve, through a selective annuloplasty, and stabilization of the entire functional aortic annulus (FAA) with reimplantation of the commissure at 180° at the level of the virtual basal ring (VBR) and sinotubular junction (STJ). Depending on the valve phenotype, additional cusp modifications are often required to address one or two prolapsing cusps and/or a fibrous raphe. With this, we have previously reported a 12-year survival rate of 94%, which is alike the general population, and also an overall freedom from aortic valve reoperation of 91%.
Cover