Twenty-five years’ experience with root remodeling and bicuspid aortic valve repair
Abstract
Background: Bicuspid aortic valves may be associated with ascending aortic aneurysm, or develop severe aortic regurgitation with variable aortic dilatation. If aortic dilatation involves the root, valve-preserving root replacement is a treatment option, and we prefer root remodeling for this purpose. The objective of this study is to review our experience encompassing 25 years.
Methods:Between November 1995 and August 2021, 472 patients (429 male; age 9–80 years; mean 48±13 years) were treated by bicuspid aortic valve repair and root remodeling. Aortic regurgitation was present in 322 cases. The primary indication for surgery was aortic regurgitation (n=317), aortic aneurysm (n=143) or acute type A aortic dissection (n=12). In 271 instances, a suture annuloplasty was added. Cusp calcification was present beyond the raphe in 80 cases, and a pericardial patch was used for partial cusp replacement in 44 cases. Follow-up was 92.8% complete with a mean of 71±68 months (median 61 months).
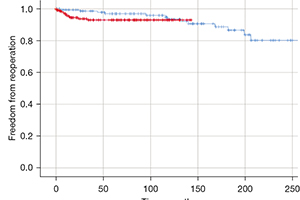
Results: Hospital mortality was 0.4% and survival at 20 years was 76.9%. Reoperation was necessary for recurrent aortic regurgitation in 26 patients; nine patients underwent reoperation for stenosis. The overall freedom of reoperation was 90.5% after ten years and 76.6% after 20 years. Annuloplasty was associated with a higher proportion of competent aortic valves at discharge (P=0.001), and had no effect on ten-year freedom from reoperation. The use of a pericardial patch for cusp repair was a predictor for reoperation (P=0.003). The presence of cusp calcification was a predictor for the development of aortic stenosis and reoperation (P=0.032).
Conclusions: Bicuspid aortic valve repair combined with root remodeling leads to excellent ten- and
20-year results. Cusp calcification and partial cusp replacement are associated with an increased probability of valve failure requiring reoperation.
Cover